Thermal Transfer Printing: What Is It, How Does It Work, And The Tech Behind It
Thermal transfer technology is a cornerstone in modern printing, offering precision, durability, and efficiency. It excels in producing high-quality, crisp images and text, with prints that are resistant to smudging, moisture, and fading.
What Is Thermal Transfer Printing Technology?
Thermal transfer is distinguished by its method of printing, where heat is applied to a wax or resin-based ribbon to transfer ink directly onto a substrate. This technique is particularly effective for creating durable prints that must withstand environmental challenges such as exposure to chemicals, weather, and physical wear.
The Basics of Thermal Transfer Printing
At its core, thermal transfer involves a thermal print head composed of many small heating elements. Each element heats up as needed, melting the ribbon’s ink and bonding it to the label material—typically made of paper, polyester, or polypropylene. This process allows for precise control over print quality and is ideal for producing both high-density barcodes and fine text.
Comparison with Direct Thermal Printing
Unlike thermal transfer, direct thermal printing does not use a ribbon. Instead, it relies on heat-sensitive materials that blacken when the printer head applies heat directly to them. While direct thermal printing is efficient and cost-effective for short-term applications like shipping labels, it lacks the durability of thermal transfer prints, which are resistant to heat, moisture, and UV light. Learn more about the difference between direct thermal vs. thermal transfer printing.
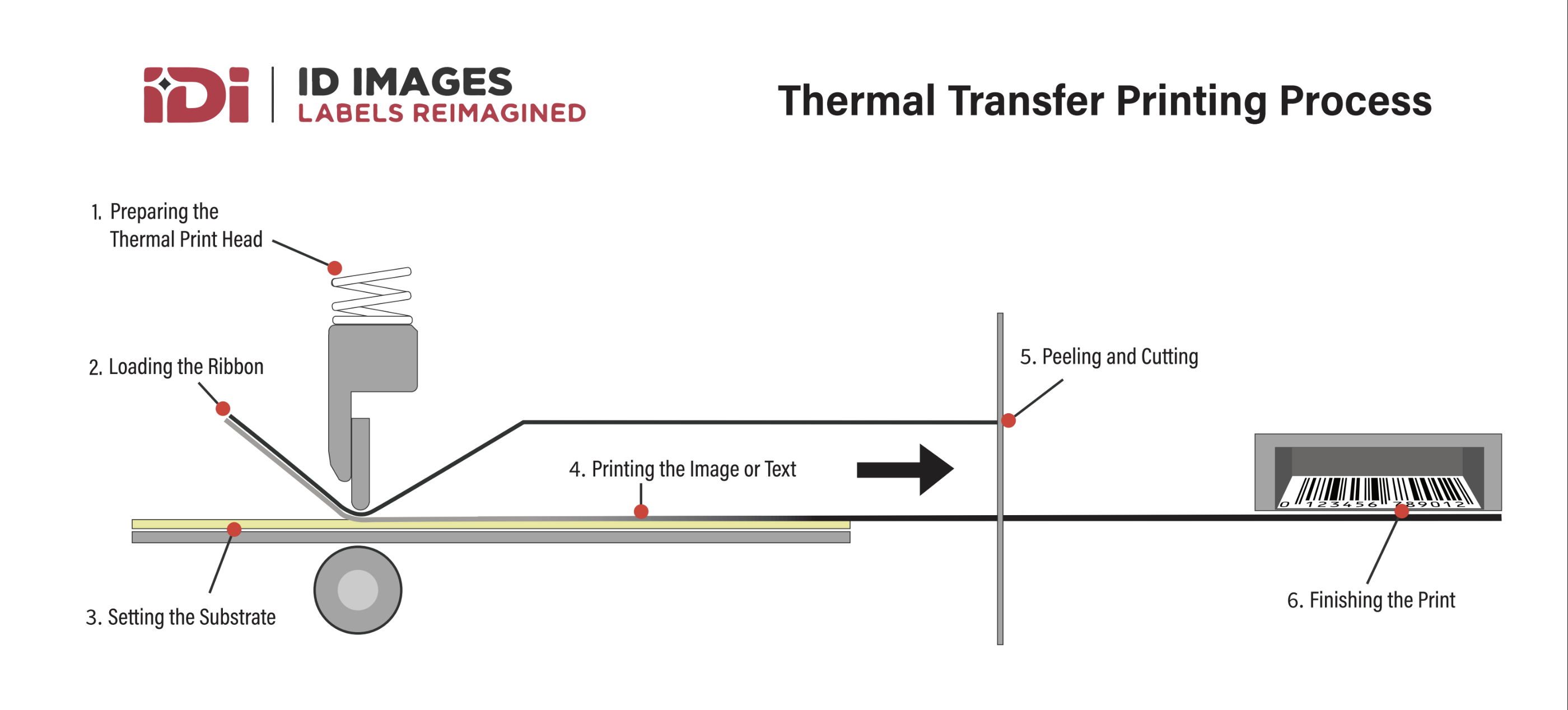
Step-by-Step Guide to the Thermal Transfer Printing Process
Thermal transfer printing is a sophisticated technology that requires precise control over various components to produce high-quality prints. Here’s a breakdown of the essential steps and key elements involved in the thermal transfer process:
1. Preparing the Thermal Print Head
The heart of a thermal transfer printer is its print head, which consists of many small, precisely controlled heating elements. These elements generate heat according to the print data received, which dictates which parts of the ribbon will transfer ink to the substrate.
2. Loading the Ribbon
A critical component in thermal transfer printing is the ribbon. Ribbons are available in different types based on the application, including wax, wax/resin, or pure resin. The choice of ribbon material affects the durability and quality of the print. The ribbon is loaded into the printer, aligned with the thermal print head.
3. Setting the Substrate
The substrate, or material to which the ink is applied, is another vital component. Common substrates include paper, polyester, and polypropylene, each suitable for different uses based on their properties. The substrate is fed into the printer, ready to receive the print.
4. Printing the Image or Text
As the print job begins, the printer synchronizes the movement of the ribbon and substrate. The thermal print head heats up and cools down rapidly, melting the ribbon’s ink and pressing it onto the substrate in the desired pattern. This process is highly precise, allowing for detailed images and sharp text.
5. Peeling and Cutting
In some thermal transfer printers, after the image or text is transferred, the ribbon (carrying the unused ink) is peeled away from the substrate, and the printed material is cut to size. This step is crucial for creating individual labels or sections.
6. Finishing the Print
The final print is often treated to ensure it sets properly on the substrate, enhancing durability against environmental factors like moisture, UV light, and chemicals. Some prints may require additional post-processing steps depending on their use.
How Various Industries Utilize Thermal Transfer
Thermal transfer printing technology is instrumental in numerous industries due to its ability to produce durable, high-quality prints on a variety of materials. Here’s how this technology is applied in different sectors:
Barcode Labels in Logistics
One of the most common uses of thermal transfer is barcode labels, essential for inventory management and logistics. These labels must withstand handling, environmental changes, and long-term storage without losing legibility, making thermal transfer the preferred choice for shipping and warehousing needs.
Textile Labeling in Apparel Manufacturing
In the textile industry, thermal transfer is used to create care labels and brand tags for clothing. These labels must endure repeated washing and friction, demands that thermal transfer technology meets with its durable resin ribbons.
Durable Labels in Electronics
Thermal transfer plays a vital role in the electronics industry, where labels are exposed to high temperatures and abrasive conditions. The precise application and chemical resistance of resin ribbons are perfect for labeling electronic components, ensuring information remains clear and legible throughout the product’s lifecycle.
Automotive Industry Compliance
The automotive sector relies on thermal transfer for creating labels that adhere to safety and regulatory requirements. These labels are used on everything from engine components to battery labels and must resist oils, solvents, and extremes of temperature.
Healthcare Applications
In healthcare, patient safety is paramount. Labels produced by thermal transfer printing are used for patient identification bracelets, specimen labels, and medication labeling, where clarity and durability can significantly impact patient care.
Retail Labeling and Branding
Retailers use thermal transfer labels for price tagging and product identification, where high-quality aesthetic prints are necessary to convey brand integrity and attract customers.
Trends and Predictions
Thermal transfer technology continues to evolve, driven by advancements in materials science, printing technology, and industry demands. Here’s what we can expect in the near future:
Integration with Digital Technologies
As industries continue to embrace digital transformation, thermal transfer technology is likely to become more integrated with digital tools and systems. This includes better connectivity with enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, improved data analytics for operational efficiency, and enhanced customization capabilities through digital interfaces.
Advances in Eco-Friendly Solutions
Sustainability concerns are pushing the development of more eco-friendly thermal transfer solutions. These advancements are not only crucial for reducing environmental impact but also for meeting the increasing consumer and regulatory demands for more sustainable practices.
- Biodegradable Ribbons: Innovations in thermal transfer ribbon technology are leading to the creation of fully biodegradable options. These ribbons are designed to decompose under specific conditions, leaving minimal environmental footprint.
- Energy-Efficient Printers: The next generation of thermal transfer printers focuses on energy efficiency. Manufacturers are leveraging advanced engineering to create devices that consume less power and reduce operational costs. These printers are engineered to maintain high-quality output while minimizing energy usage, significantly reducing the carbon emissions associated with printing operations.
- Recycling and Reuse Programs: A growing trend in the industry is the establishment of programs dedicated to the recycling of used ribbons and the refurbishment of outdated equipment.
- Use of Sustainable Materials in Substrates: There is an increasing shift towards using substrates made from recycled materials or sustainable sources. These substrates are not only environmentally friendly but also offer compatibility with thermal transfer printing, ensuring that businesses do not have to compromise on quality for sustainability.
Enhanced Print Quality and Speed
Continual improvements in print head technology and ribbon formulations are expected to enhance both the quality and speed of thermal transfer printing. Innovations might include faster print heads that do not sacrifice resolution or clarity, allowing businesses to increase productivity without compromising on print quality.
Expansion into New Markets
As the technology advances, thermal transfer printing is likely to find new applications in markets that have not traditionally relied on this method. This could include sectors like consumer electronics, where durable and precise labeling is increasingly critical, and in emerging markets where manufacturing growth demands robust labeling solutions.
More Robust and Versatile Printers
Future thermal transfer printers are expected to be more robust and versatile, capable of handling a wider range of materials and environmental conditions. This will allow for greater flexibility in how and where thermal transfer technology can be used, broadening its applicability across different industries.
Further Reading and Resources
To deepen your understanding of thermal transfer printing technology and explore its various applications and advancements, we recommend the following resources and related topics:
In-Depth Studies and Resources
- The Future of Thermal Printing to 2027: Thermal printing markets will continue to be driven by well-established technology and business sector trends. Read the report at Smithers Pira.
- Thermal Printing Market Analysis: Future Market Insights offers a report covering market trends, growth drivers, and technological advancements that are shaping the future of thermal printing across various industries. Explore the comprehensive market analysis.
- Opportunities in Sustainable Thermal Transfer Printing: Smithers examines the shift towards sustainable practices within the thermal transfer printing industry, highlighting innovations that reduce environmental impact. Learn about the opportunities in sustainable printing.
Recommended Reads on Thermal Transfer Technology
- Selecting the Perfect Ribbon for Your Needs: Gain a clearer understanding of the distinctions between various types of ribbons—wax, wax/resin, and resin—and determine which type suits your specific printing requirements. This guide is invaluable for those looking to optimize their printing processes. Read the full guide on selecting the perfect ribbon for your needs.
- Current Trends Shaping Product Labeling: Explore how the latest advancements in product labeling are influencing printing technology choices, with an emphasis on sustainable and efficient practices. This read is crucial for staying ahead in the dynamic field of product labeling. Dive into current trends shaping product labeling.
Connect with a Thermal Transfer Expert
Interested in elevating your labeling strategies with thermal transfer printing technology? Speak with a thermal transfer expert at ID Images to explore the right labels and printing supplies tailored to your specific needs.